Computed tomography
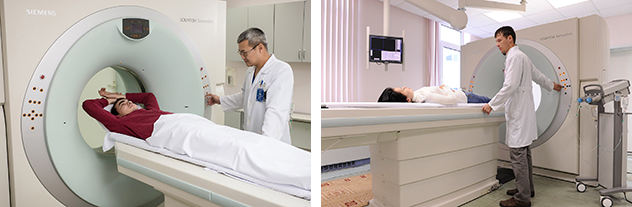
Computer tomography allows the study of all the departments and systems of the body, both native and using contrast agents, including special software packages to determine the extent of coronary heart arteries with atherosclerosis, the definition of mineral density of bone tissue in cases of suspected osteoporosis, panoramic reconstruction images of the upper and lower jaw (similar to orthopantogram).
A list of proposed survey techniques for multi-slice CT is very wide, this also contributes to the availability of additional tools such as x-ray contrast agents (only used nonionic x-ray contrast agents) and automated syringe for accurate dosing. Intravenous contrast agents required for research vessels, in cases of suspected tumor. The quality of the computer tomogram using different programs was highly appreciated by leading specialists of the University clinic of Freiburg. Started in 2015 with the introduction of protocols with reduced radiation exposure to the patient.
The main indications for the Research conducted in the Department:
CT of the brain:
- Stroke native and urgently at the possibility of thrombolysis;
- After 6-10 hours from the start of the clinic at impossibility of thrombolysis;
- Urgently with suspected hemorrhage;
- Head trauma accompanied by cerebral symptoms;
- Planning at the control investigations, the suspicion on volumetric process, hydrocephalus, macro-and microangiopathy, developmental abnormalities, and epilepsy.
- suspected bone diseases, osteoporosis, herniated disc.
- urgent trauma with complaints of
Abdominal organs:
-
urgent trauma, suspected bleeding, calculus of the urinary tract, acute inflammatory processes (abscess, appendicitis, diverticulitis, pancreatitis), acute intestinal obstruction;
-
planning - if you suspect that the volumetric processes of the abdominal organs, control studies
Vascular:
-
urgently with suspected artery occlusion, bleeding;
-
planning in the refinement of anomalies, assessing the degree of narrowing of the vessel lumen (the lumen diameter of the vessel to 1.5 mm).
Head CT:
The study of the brain:
A) program visualization (Native or with the use of a contrast agent. Thin slices of the brain – 1.0 mm, the smaller the radiation dose, long scan)
B) traumatic injuries (Native. Thin cuts on the bone structure of -1.0 mm, quick scan)
C) the Study of the inner ear (Native, only the area of the inner ear, in bone only mode, shear 0.6 mm)
G) Examination of the paranasal sinuses (Native or with contrast material. Only the area of the paranasal sinuses)
D) Research in the cardiovascular mode (Only with contrast. Study of the arteries in the vascular window 0.6 cm)
E) contrast Study of the parenchyma (Only with contrast, is evaluated only parenchyma)
G) the Study of the orbits (Native or with contrast medium, only the area of the orbits)
H) 3D – pentagramma (Native, only the upper and lower jaw
The examination of the cervical region:
A) examination of thyroid (native or with contrast material. The area from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery up to the tops of the lungs)
B) the Study of the larynx and pharynx (Native or with contrast material. The area from the nasopharynx to the tops of the lungs)
Examination of the joints:
The study of bone pathology (case of aseptic necrosis), pre - and postoperative studies (native, the joint area)
Examination of organs of thorax:
A) According to the program PE (Only with contrast in the phase contrast enhancement of pulmonary arteries)
B) the elimination of the tumor (Only with contrast in the phase contrast pulmonary veins)
C) the Study of the esophagus (Only with contrast per os and intravenous)
G) Study to determine the presence of occupational diseases (Native)
D) Assessment of patency of the bronchial system, the exclusion of inflammatory and other changes in the parenchyma of the lung (Native mode CARE Dose)
Examination of organs of abdominal cavity:
A) the Exclusion of space-occupying lesions of the parenchymatous organs, inflammatory changes in the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space (only with contrast in the arterial and venous phases)
B) excluding calculi of the kidneys, urinary tract, common bile duct and gall bladder (native mode CARE Dose)
C) the Study of the adrenal gland (Only with contrast in arterial, venous and delayed phases)
G) examination of stomach, duodenum and pancreas (With the introduction of contrast medium/water per os and, possibly a contrast agent intravenously. With the use of muscle relaxant, special styling)
D) the study of the lumen and wall of the intestine (With the introduction of contrast medium per rectum and possibly intravenously. With the use of muscle relaxant)
E) Virtual colonoscopy (using muscle relaxant, the introduction of air per rectum)
Examination of the spine
The study of the skeletal system:
A) subject To traumatic injuries, or focal changes
B) the Study of the skeleton in multiple myeloma
C) Densitometry (using special mattress)
Vascular:
A) the study of the anomalies of the vascular system
B) Investigation of suspected thrombosis of the artery
D) Ca-Scoring (native)
D) Study of blood vessels of the heart
Puncture and biopsy:
A) Puncture of the soft tissues and parenchymatous organs
B) Puncture of the bone structure
C) formulation of the drainage