Ultrasound examination
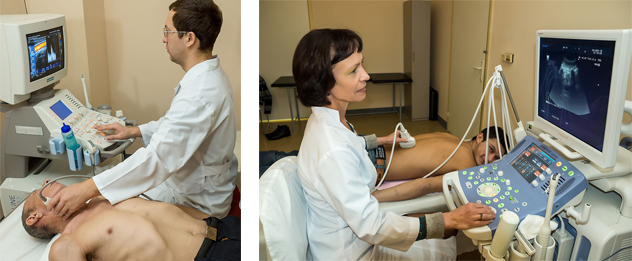
An echocardiogram (also called an echo) is a type of ultrasound test that uses high-pitched sound waves that are sent through a device called a transducer. The device picks up echoes of the sound waves as they bounce off the different parts of your heart. These echoes are turned into moving pictures of your heart that can be seen on a video screen.
The different types of echocardiograms are:
- Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE). This is the most common type. Views of the heart are obtained by moving the transducer to different locations on your chest or abdominal wall.
- Stress echocardiogram. During this test, an echocardiogram is done both before and after your heart is stressed either by having you exercise or by injecting a medicine that makes your heart beat harder and faster. A stress echocardiogram is usually done to find out if you might have decreased blood flow to your heart (coronary artery disease).
- Doppler echocardiogram. This test is used to look at how blood flows through the heart chambers, heart valves, and blood vessels. The movement of the blood reflects sound waves to a transducer. The ultrasound computer then measures the direction and speed of the blood flowing through your heart and blood vessels. Doppler measurements may be displayed in black and white or in color.
- Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE). For this test, the probe is passed down the esophagus instead of being moved over the outside of the chest wall. TEE shows clearer pictures of your heart, because the probe is located closer to the heart and because the lungs and bones of the chest wall do not block the sound waves produced by the probe. A sedative and an anesthetic applied to the throat are used to make you comfortable during this test.
Echo can be used as part of a stress test and with an electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) to help your doctor learn more about your heart.
Do not eat heavily for a few hours before a stress echo to help prevent nausea. You may feel nauseated if you exercise with a full stomach or from the injection of dobutamine.
Wear flat, comfortable shoes (no bedroom slippers or sandals) and loose, lightweight shorts or sweatpants for an exercise stress echo.
Ask your doctor whether you should take your regular medicines as usual. Tell your doctor if you take insulin.
3. Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
Do not eat or drink for at least 6 hours before the TEE
If you have dentures or dental prostheses, you may need to remove them before the test.
If you have medical problems involving the throat, esophagus, or stomach, tell your doctor before getting this test.
Before a TEE, you will be given a sedative. You will not be able to drive for at least 12 hours after the procedure. Be sure to make arrangements in advance for someone to pick you up after the test.
Before an echocardiogram, you may be asked to sign a consent form that says you understand the risks of the test and agree to have it done.
Talk to your doctor about any concerns you have regarding the need for the test, its risks, how it will be done, or what the results will mean.
.
Ultrasonic duplex scanning of the arteries, veins extremities, aortic arch branches (the brachiocephalic vessels) is an ultrasonic method of investigation of these vessels. This non-invasive method is to obtain ultrasonic images of blood vessels and blood flow on the screen of the device by applying the ultrasonic probe to the body surface in the projection of the corresponding vessel. Is performed most often to detect and assess the severity of atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries, diagnosis of thrombosis and valvular insufficiency of the veins, there are other more rare indications for research.
Special training is required (except for the study of the branches of the abdominal aorta, Vena cava). Has virtually no risks and complications, as it is a non-invasive method. Alternatives to study: angiography, contrast CT and MRI of blood vessels, other.
Neurosonography – method study of the brain in newborn through large and small fontanelles and definition of the various forms of damage to the nervous system in newborns. Special training is required. Before the examination it is advisable to feed the baby, so he was calm. Has no radiation exposure. Alternative study: computed tomography of the brain.
Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder is performed using the following methods: transabdominal (through the anterior wall of the abdomen), and transrectal (through the rectum). More informative transrectal method that allows to visualize the smallest changes in the structure. Indications for ultrasound of the prostate: pathology, detected by rectal digital examination, any urination disorders, clinical manifestations of acute and chronic renal failure, changes in blood and urine. Required preparation: before the procedure it is necessary to clean the intestines (the night before to do an enema or drink a laxative). Ultrasound can be with a full bladder (1.5 hours before the test drink a liter of water without gas).
Ultrasound of the scrotum. Method of the study structure of the scrotum using ultrasound. It is not an invasive procedure performed to diagnose abnormalities of the testicles, non-neoplastic diseases (dropsy, cysts, varicocele, inguinal hernia, inflammatory diseases of the testicles), testicular tumors.
Pleural ultrasound of the sinuses is performed to identify the pathological effusion, which often accompanies many pathological processes in the pleura, lung, mediastinum, and diaphragm. Training is not required.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity is one of the types of non-invasive study of the human body by use of ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is performed through the abdominal wall condition the shape and size of organs, changes in the structure of tissues, developmental abnormalities, acquired diseases. Using a procedure it is possible to recognize acute and chronic inflammation, stones and tumors. Abdominal ultrasound (examination through the abdominal wall) is used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, and also performed prophylactically. During the inspection of the liver revealed cirrhosis, hepatitis, cysts, abscesses. Based on the parameters of the gallbladder, the doctor confirms or denies such diagnoses as deformation in the structure, inflammation. On the examination is determined by the size of the spleen and abnormalities.
The procedure is absolutely painless. The contact sensor is covered with a special conductive gel. The survey is conducted in the supine position on the back, if necessary, the doctor may ask you to roll over on its side, and hold your breath for a few seconds.
For successful ultrasound scan is necessary to observe for a half or two days of the diet, aimed at removing or reducing flatulence (especially if there is a patient recent). For this purpose from the diet is desirable to eliminate foods that cause excessive gas production: raw vegetables and fruits, legumes, sauerkraut, juices, brown bread, whole milk, and carbonated beverages. To reduce intestinal gas production take enzyme preparations or infusion of chamomile. Patients with chronic constipation, it is recommended enema. The study itself should be conducted in fasting for 8-12 hours is optimal on an empty stomach after the morning fasting. There are no risks and complications. Alternatives to study: contrast CT and MRI.
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys is one of the most informative methods of examination for diseases of the urinary system.
Ultrasound of the kidneys allows you to determine their size and location, tissue structure, blood flow velocity blood vessels, the presence of sand and stones.
Normal kidneys are located on both sides of the spine at the level of the 12 thoracic vertebrae. They are surrounded by adipose tissue. Kidney tissue is homogeneous. In the cavity of the body cannot be sand and stones. The kidney on the right side is a little lower on the left. The deviation of the location or size of the norm indicates pathologies. The increase in size suggesting inflammation, decrease of degenerative changes, serious chronic diseases. Special training is required. Alternatives to study: contrast CT and MRI.
Thyroid ultrasound allows you to track the status of this important body and its surrounding lymph nodes and time to notice disturbing changes in their States (increase, nodular tumors, cysts) and functioning. This is especially important for residents of ecologically unfavorable areas. The procedure is carried out in the supine position, the patient lies on her back with her head thrown back In the case where the patient have problems with the cervical spine or physical condition does not allow him to take the right supine position, to conduct a study can be sitting. Special training is required. There are no risks and complications, as it is a non-invasive method. Alternatives to study: contrast CT and MRI.
Ultrasound of soft tissues is used to identify hematomas , lipomas , neoplasms. Examination of soft tissue allows to determine the size and nature of tumors and blood flow in the area of the tumor. This study is a safe and effective method which can be carried out repeatedly within a short period of time. Special training is required.
Gynecological ultrasound
ULTRASOUND examination of the PELVIC ORGANS (uterus, ovaries and bladder)
Purpose: examination of organs of small pelvis.Indications:
- pain in the pelvis;
- relapsing inflammation in adults; acute infection in children;
- palpable education in the pelvis, a suspected tumor of the uterus and/or ovaries;
- anomalies of development of organs of small pelvis;
- dynamics of follicle growth to determine causes of infertility (FOLLICULOGENESIS);
- fever of unknown origin, especially in combination with pain in the lower abdomen;
- clarification of the presence and location of an intrauterine contraceptive.
Indications for ultrasound of the pelvic organs in case of emergency:
-
diffuse abdominal pain and/or pain in the lower abdomen;
-
uterine bleeding;
-
acute urinary retention;
-
abdominal trauma, suspected the presence of free fluid in the pelvic cavity.
For emergency and routine ultrasound contraindications do not exist.
Transabdominal sonography – an ultrasound of the pelvic organs through the abdominal wall: the bladder should be filled. Patient give to drink 4-5 glasses of liquids, the study was conducted in an hour (not allowed to urinate). If necessary, the filling of the bladder can be made via the urinary catheter with sterile saline solution.
Transvaginal ultrasonography - ultrasound examination of small pelvis organs directly through the vagina, a special vaginal probe. To create a good contact of the sensor with the target surface a special rubber cover (or condom) put a sufficient amount of gel; a condom is necessary and to prevent infection. This technique is very informative for the diagnosis of early pregnancy and diseases of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovarian formations, including ectopic pregnancy.
When applying this technique, the bladder should be empty. Patient it is recommended that more careful preparation is necessary before the study do a cleansing enema.
ULTRASOUND STUDIES DURING PREGNANCY
Ultrasound in obstetrics has been used for nearly 30 years. Although it is believed that ultrasound is virtually harmless, but, nevertheless, still be performed to confirm this position. Sonography (ultrasound) is the most important tool of screening for pregnant women and can be used according to clinical indications in any pregnancy.
There is no need to conduct the ultrasound examination every month and at each visit of the pregnant physician, except in those cases when the Clinician has reason to suspect a pathology requiring follow-up.
A screening ultrasound, or a scientific prenatal sonography – is a planned study of pregnant women, regardless of their age, presence of any systemic diseases or risk factors. The main objective of screening is prenatal diagnostics of congenital and hereditary diseases in the fetus.
A screening study includes three compulsory examinations. The first study conducted on the period from 10 weeks to 13 weeks 6 days to confirm pregnancy and determination of its term. But most importantly, it was during this period revealed the presence of chromosomal anomalies, such as Down syndrome or Turner syndrome. Measured the thickness of the neck area (thickness of skin folds in the neck). It is scientifically proven that the thickening of the folds of more than 3 mm found in the chromosomal anomalies. Also in this period reveals gross violations of the anatomy of the fetus, for example, pathology of the Central nervous system or skeletal dysplasia.
A second study conducted during the period 20-24 weeks and is the most responsible. During this period, revealed the majority of malformations, fetal hereditary diseases. This study is conducted on a special form, where the doctor has specific tasks as the analysis of the anatomy of the fetus, i.e., the development and detection of defects of all organs and systems of the fetus. This study (especially for women from high-risk groups) should be conducted in specially equipped centres for prenatal.
The third screening at 30-34 weeks is carried out with the purpose of diagnosing malformations detected at a later period, these include, for example, malformations of the urogenital system. These vices are called vices with late manifestation. It also assesses the development of the fetus, according to the clinical term of the pregnancy, amount of amniotic fluid is estimated utero-placental blood flow (as indicated).
Determination of fetal sex is not an indication for ultrasound, with the exception of cases with a history associated with the floor of hereditary disease.
The preparation of the study. For ultrasound during pregnancy in the II and III trimester additional training the patient is required. The research was conducted in the supine position or on its side in a relaxed, calm state, with an emptied bladder, TRANS abdominal transducer (i.e. through the abdominal wall). For ultrasound in the first trimester (early pregnancy) to improve visualization sometimes requires filling the bladder (to drink 4-5 glasses of fluid, not pee, a study is carried out in an hour), or conducting a TRANS vaginal ultrasound (i.e., through the vagina with a special sensor). The first screening study is also preferably performed transvaginal probe, especially in patients with high-risk patients with severe subcutaneous fat. The bladder should be emptied.
Vascular Doppler ultrasound of the fetus
Additional ULTRASONIC examination carried out during pregnancy, solely on the testimony of the observing obstetrician. Is performed in the third trimester (after 30 weeks) with such conditions as the syndrome of delayed fetal development, with RH conflict – risk of developing auto-immune hydrops of the fetus, multiple pregnancy, especially when monochorionic pregnancy (risk of development of Feto-fetal syndrome). Preparation for this examination are required. All the research is conducted as well as the usual ultrasound during pregnancy. Fruit investigated the blood flow in the arteries of the umbilical cord of the fetus, placental blood flow in uterine arteries. Doppler ultrasound is not dangerous for the pregnant woman or fetus and carried out if indicated, is of great clinical significance.
ULTRASOUND examination of mammary glands
Indications for ULTRASOUND research:
differentiation of a solid (tissue) formations from cystic;
differentiation of cancer from benign neoplasms, identified during the initial investigation and/or x-ray mammography;
an independent method of diagnosis during the initial examination of young, pregnant and lactating women with symptoms of breast disease.
The study of breast is advantageously carried out in the first half of the menstrual cycle (6 to 9 days). Before the examination careful palpation of the mammary glands, knowledge of the data prior x-ray mammography, the medical history of the patient. Ultrasound is performed in the supine position with head behind hands. With a large volume of the mammary glands should study first the one breast with the rotation of the patient on the polubok, then turn on the other polubok with selegenenko over the head with her hand with the test side.
In identifying tumors of uncertain nature should determine its vascularization (i.e., to assess the blood flow in the formation using color Doppler). In the case of malignant breast tumors need to Supplement standard survey scan over-and subclavian areas.
Additional training to conduct ULTRASONIC research of mammary glands from patients is not required.
ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION OF THE JOINTS
With the help of modern ultrasound scanners it is possible to obtain a diagnostic image of the ligaments, tendons, cartilage and muscles, comparable in information content from anatomic drugs.
THE KNEE JOINT
Indications for ULTRASOUND study
-
degenerative diseases of the joint;
-
inflammation of the tendons of the joint;
-
suspicion of the presence of fluid in the joint cavity (inflammatory or blood in trauma);
-
suspected damage to the meniscus, lateral cruciate ligament;
-
suspected dislocation of the knee joint;
-
search of fracture of the patella;
-
osteochondropathy;
-
tumors of the bones forming the joint.
THE SHOULDER JOINT
Indications for ULTRASOUND study
-
degenerative diseases of the joint;
-
inflammation of the tendons of the joint;
-
suspicion of the presence of fluid in the joint cavity (inflammatory or blood in trauma);
-
suspected damage to the rotator cuff;
-
suspected dislocation of the head of the tendon of the biceps muscle;
-
suspected dislocation or rupture of the posterior lip;
-
the changes in fractures of the bones forming the joint;
-
tumors of the bones forming the joint.
ULTRASONIC examination of the joints is carried out without special training patients. In all cases, more informative for the detection of joint pathology is conducting magnetic resonance imaging